Wilson Disease Lab Findings
Wilson disease lab findings. Wilson disease is an autosomal recessive disorder which means it takes two copies of a disease-causing pathogenic variant one inherited from each parent to cause the disorder. People with Wilson disease may have lower than normal blood copper levels. Typically the liver releases excess copper into the bile.
Most commonly patients present with progressive neurologic. The authors used proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy MRS in 37 patients with newly diagnosed Wilson disease to identify the pathomechanism. Urine copper is high.
Liver copper a liver tissue biopsy collected to help diagnosis. The copper concentration measured in a liver biopsy specimen. Wilson disease is a rare inherited disorder.
The copper deposits in. Should be considered in patients aged 10 to 40 years with hepatitis. This article aims to discuss the central nervous system manifestations of this condition.
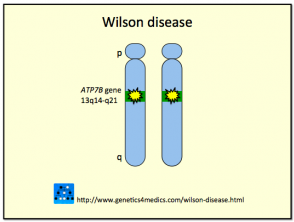
Wilson disease WD is a rare inherited genetic disorder caused by variants in the ATP7B gene that result in copper accumulation in the body particularly in the liver brain and eyes. Individuals with WD lack the necessary enzyme that facilitates clearance of copper from the liver to bile. Liver enzymes alanine transaminase ALT and aspartate transaminase AST.
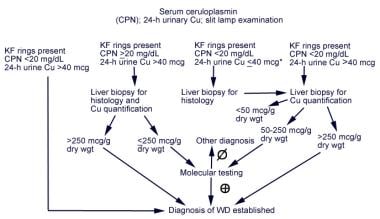
Wilson disease also known as hepatolenticular degeneration is a multisystem disease due to abnormal accumulation of copper. Listed below are the standard laboratory tests used to diagnose Wilsons disease. Impaired biliary copper excretion leads to accumulation of copper in several organs most notably the liver brain and cornea.
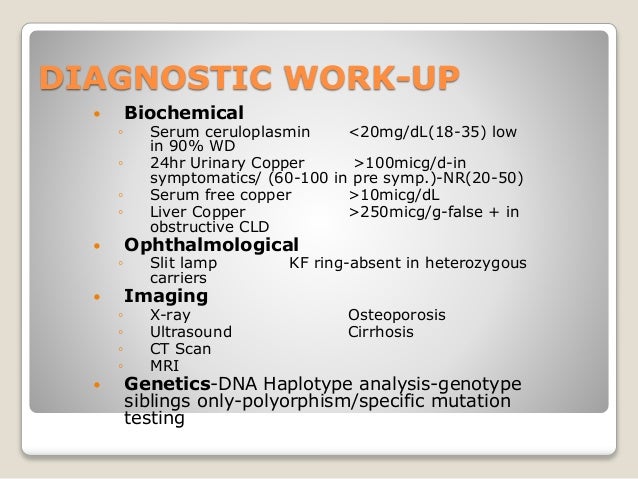
24-hour urine copper used to diagnose and monitor usually increased in Wilsons disease. Free serum copper non-caeruloplasmin-bound used to diagnose and monitor usually increased in Wilsons disease.
If the score is 4 the diagnosis of Wilson disease is very likely.
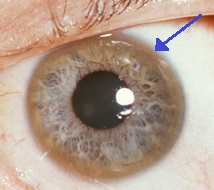
Free serum copper non-caeruloplasmin-bound used to diagnose and monitor usually increased in Wilsons disease. If you have only one copy of a pathogenic variant you are a carrier and can pass the genetic variant on to your children but you do not have symptoms of the disease. Wilson disease hepatolenticular degeneration is an autosomal recessive defect in cellular copper transport. If both parents carry a defective gene for Wilson disease there is a 25 chance in each pregnancy that the child will have the disorder. It is characterized by early onset liver cirrhosis with CNS findings most frequently affecting the basal ganglia and midbrain. Acute liver failure due to Wilson disease may cause high blood copper levels. Affects up to 1 in 40000 people. Free serum copper non-caeruloplasmin-bound used to diagnose and monitor usually increased in Wilsons disease. Symptoms including Kayser-Fleisher rings liver disease neurologic findings and psychiatric disease may present at any time from early childhood to late adulthood.
Wilson disease WD is an autosomal recessive disorder that results from the bodys inability to excrete excess copper. The authors used proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy MRS in 37 patients with newly diagnosed Wilson disease to identify the pathomechanism. RESULTS Twenty two patients presented with liver manifestations eight with fulminant hepatic failure and 14 with chronic liver disease three with neurological disease and one with haemolysis. To overcome the diagnostic challenge several clinical signs Kayser-Fleischer rings neurologic symptoms and laboratory features copper in serum urine liver. Wilsons disease is uncommon and the diagnosis is often missed. People with Wilson disease may have abnormal ALT and AST levels. It is characterized by early onset liver cirrhosis with CNS findings most frequently affecting the basal ganglia and midbrain.









































Post a Comment for "Wilson Disease Lab Findings"