Respiratory Bronchiolitis Interstitial Lung Disease Long Term Outcome
Respiratory bronchiolitis interstitial lung disease long term outcome. Respiratory bronchiolitisinterstitial lung disease. Few cases have been reported in the literature and no studies have been carried out on the effect of treatment which currently consists of smoking cessation with or without corticosteroids. A clinicopathologic study in current smokers ex-smokers and never-smokers.
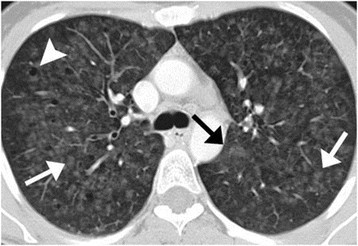
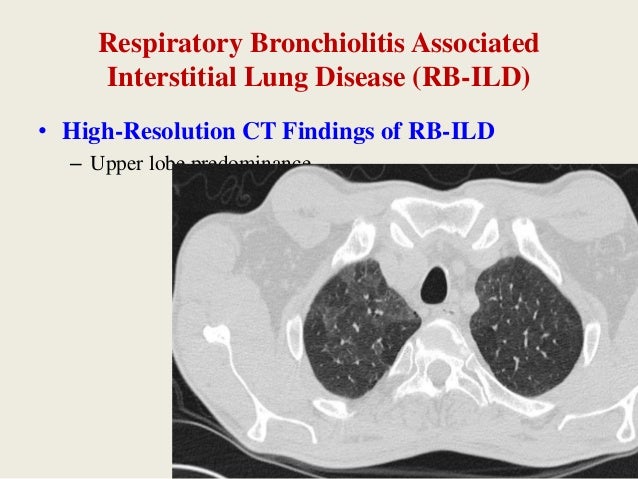
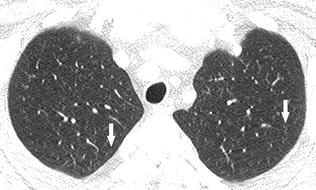
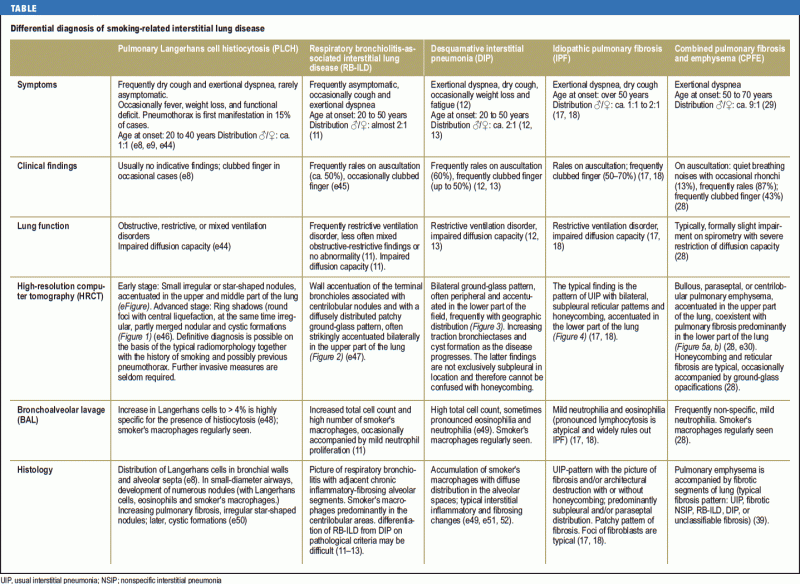
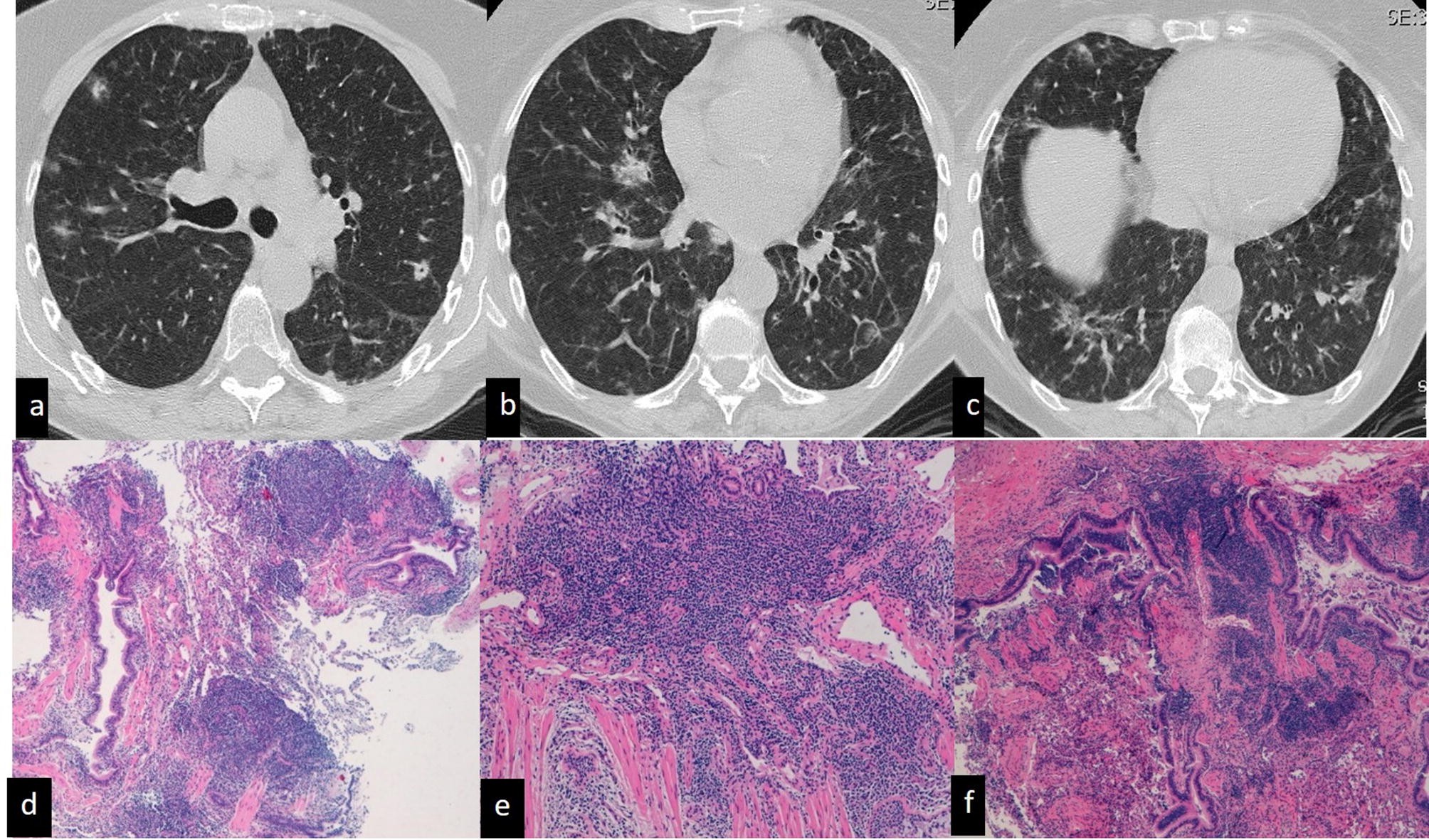
To improve the long-term survival of patients with ARS-ILD novel therapies beyond CS and IS that can prevent refractory fibrosis progression and AE development are required. Respiratory bronchiolitis associated interstitial lung disease RB-ILD is a recently described clinicopathological entity that occurs almost exclusively in current heavy cigarette smokers. And include in order of frequency central bronchial wall thickening 90 peripheral bronchial wall thickening 86 centrilobular.
Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease. Portnoy J Veraldi KL Schwarz MI et al. Respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung disease.
McWilliams AM Lake FR. Treatment is smoking cessation. Portnoy J Veraldi KL Schwarz MI Cool CD Curran-Everett D Cherniack RM King TE Jr Brown KK.
Respiratory bronchiolitis-interstitial lung disease. The majority of published reports consider RB-ILD to be a nonprogressive ILD that clinically improves with smoking cessation and antiinflammatory treatment. Portnoy J et al.
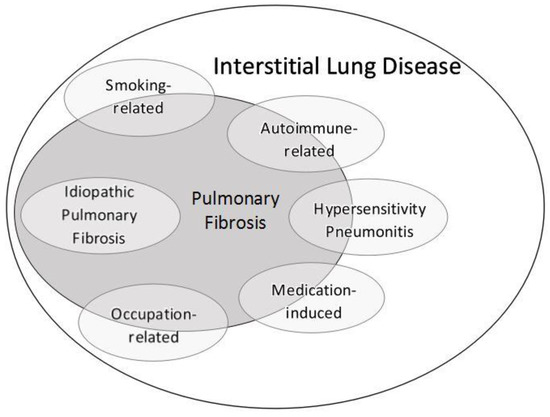
It is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia associated with smoking. Respiratory bronchiolitisassociated interstitial lung disease RBILD is a syndrome of small airway inflammation and interstitial lung disease occurring in smokers. Article PubMed Google Scholar 14.
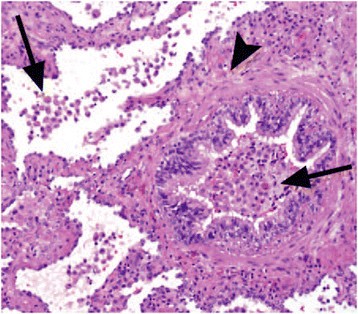
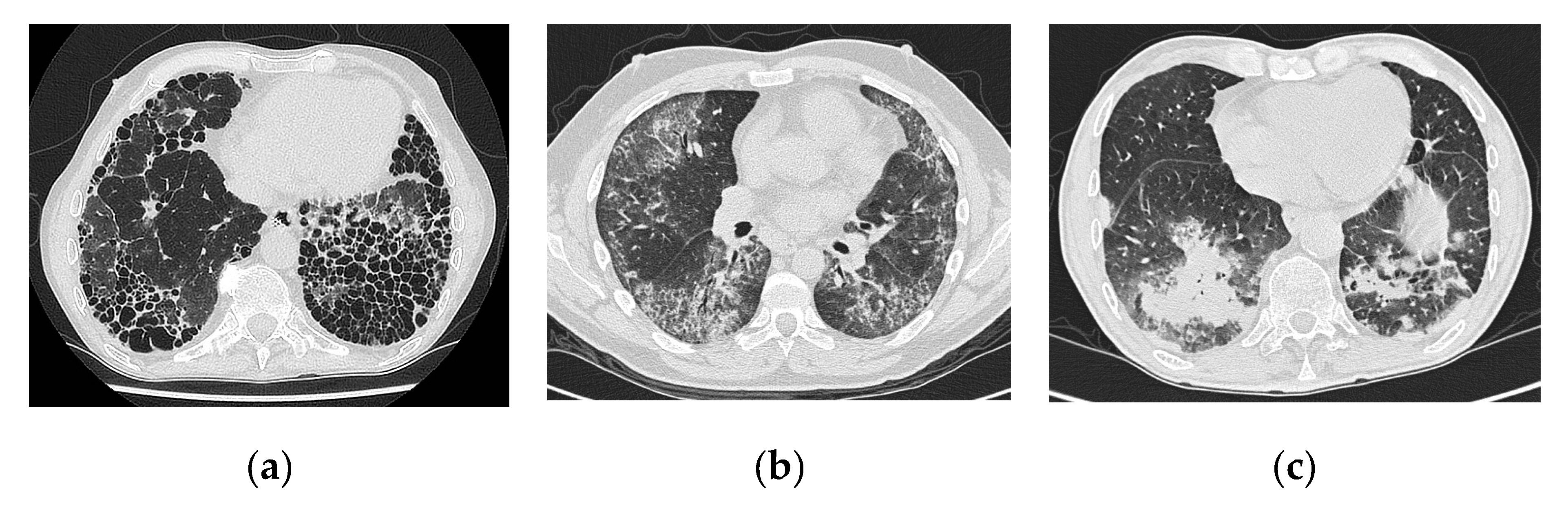
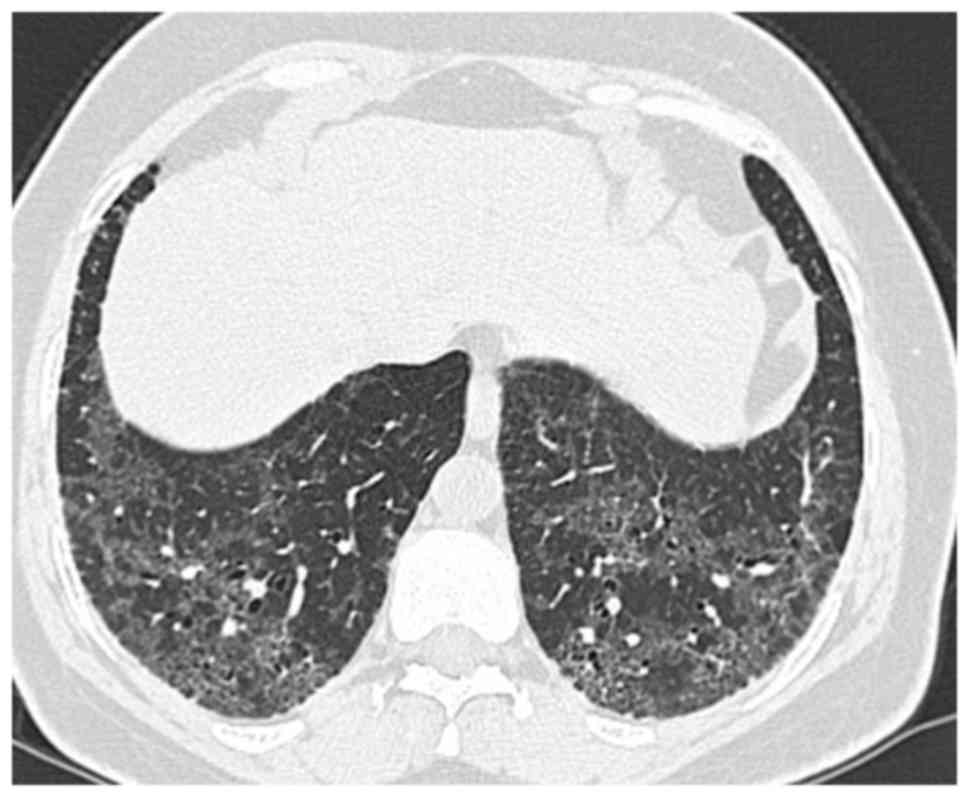
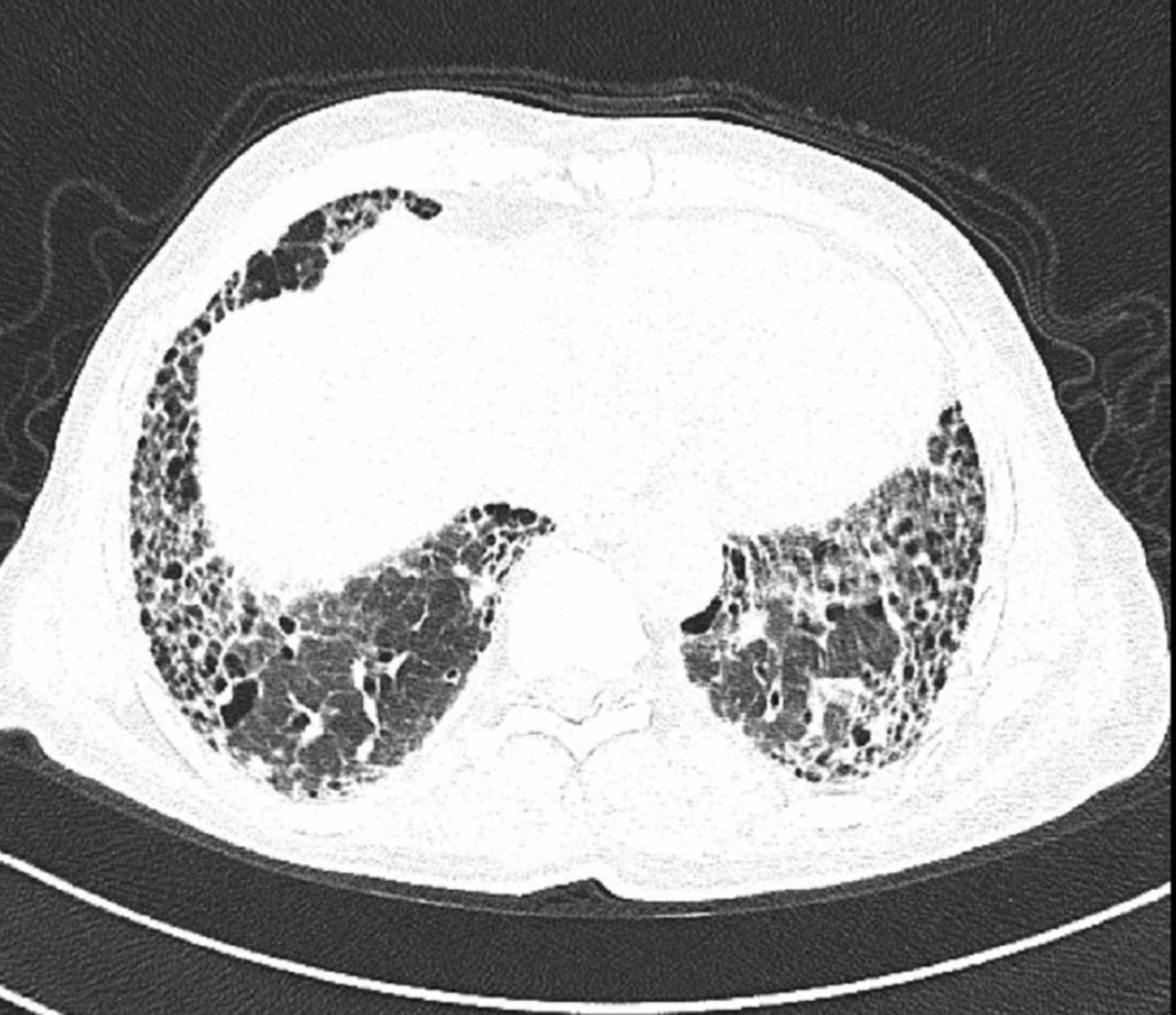
The clinical and physiologic features of respiratory bronchiolitis RB-interstitial lung disease ILD have been previously described. In a subset of patients however this is the only pathologic finding and seems to account for clinical interstitial lung disease.
Few cases have been reported in the literature and no studies have been carried out on the effect of treatment which currently consists of smoking cessation with or without corticosteroids.
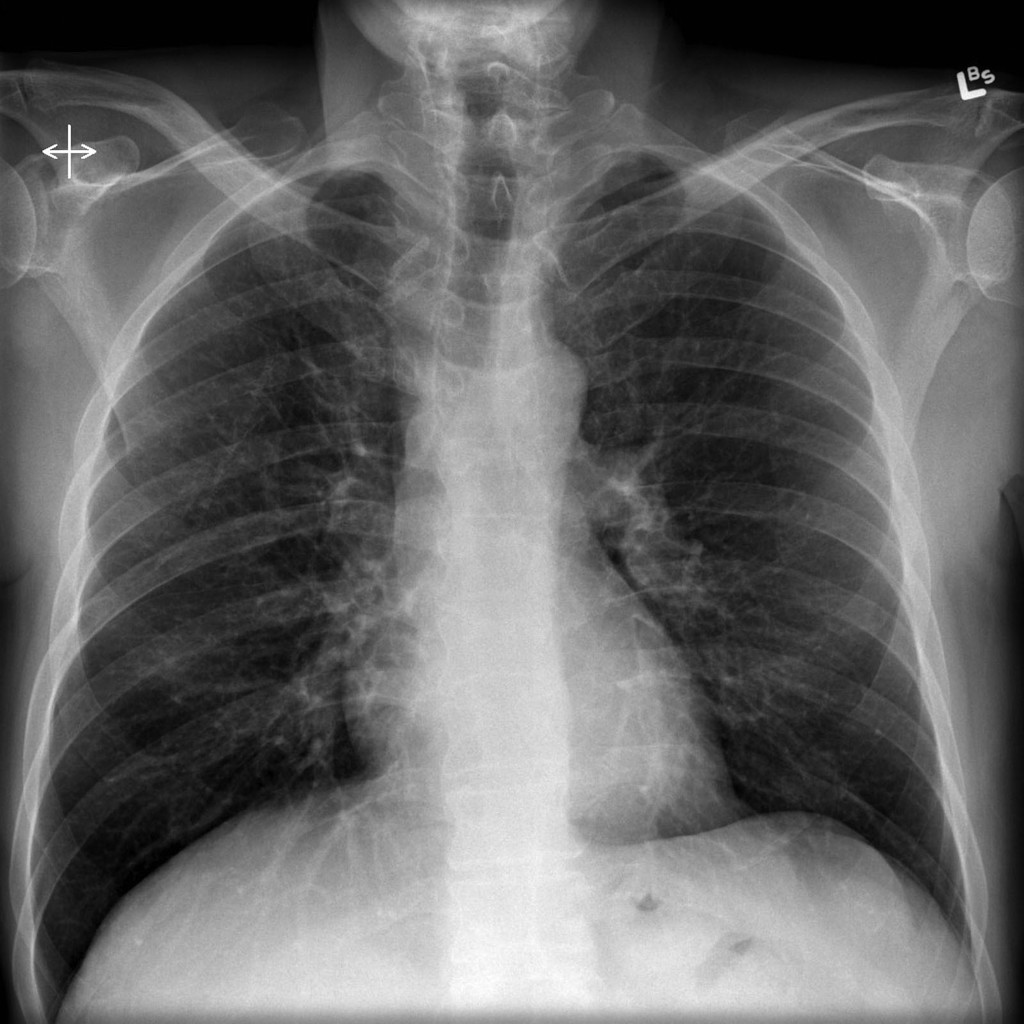
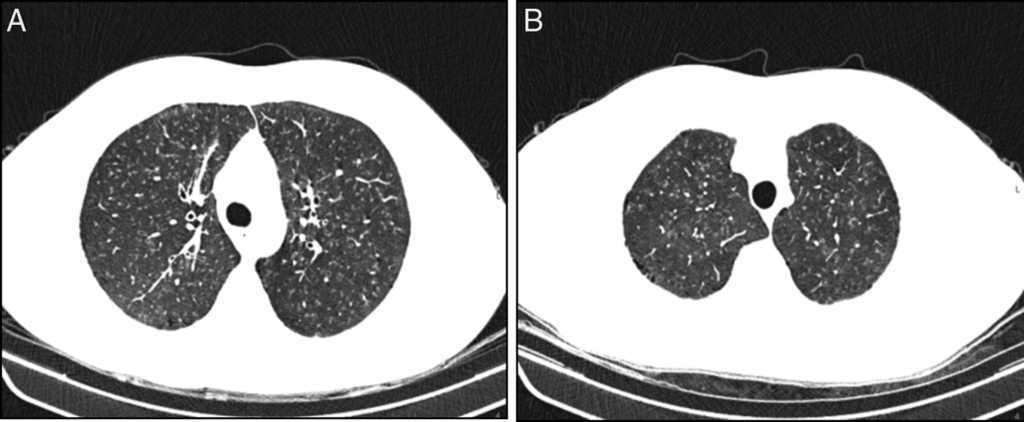
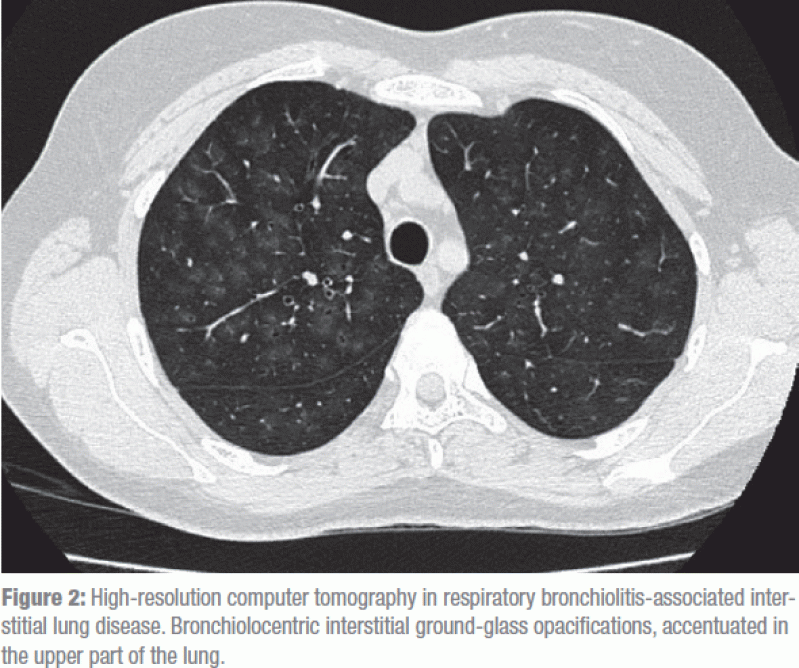
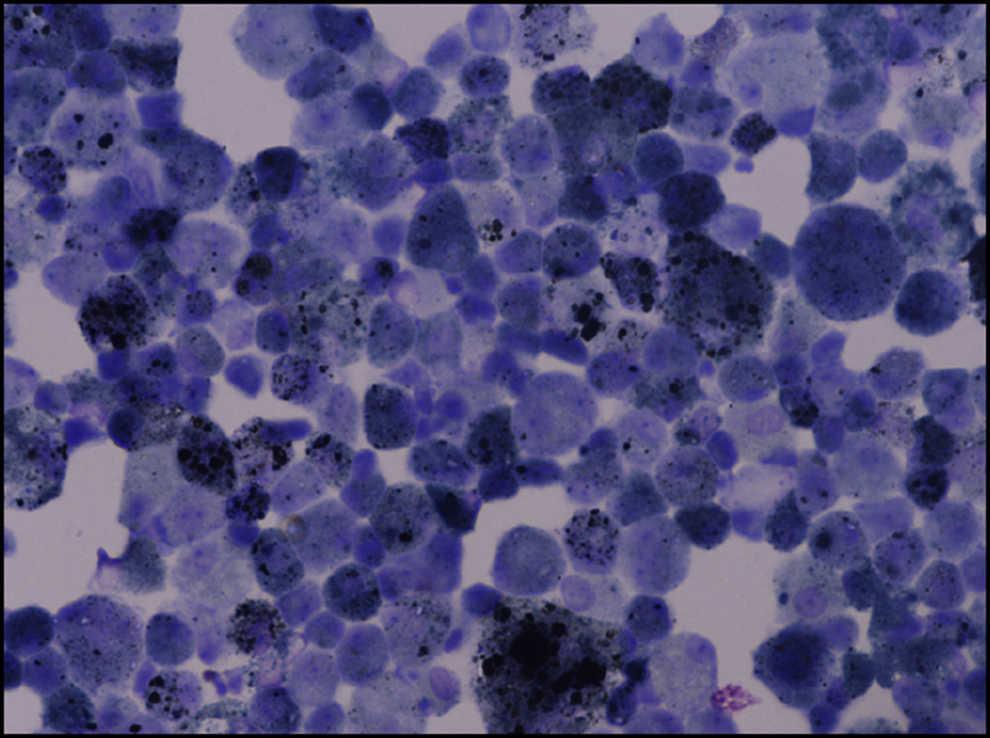
It is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia associated with smoking. The clinical and physiologic features of respiratory bronchiolitis RB-interstitial lung disease ILD have been previously described. In a subset of patients however this is the only pathologic finding and seems to account for clinical interstitial lung disease. Few cases have been reported in the literature and no studies have been carried out on the effect of treatment which currently consists of smoking cessation with or without corticosteroids. Respiratory bronchiolitis refers to a histological finding that can be often seen in heavy smokers. Symptoms include cough and breathlessness during exertion. The concept of RBILD has changed over time with the recognition that histologically and radiologically RB and RBILD are usually indistinguishable. Portnoy J Veraldi KL Schwarz MI Cool CD Curran-Everett D Cherniack RM King TE Brown KK. Respiratory bronchiolitisassociated interstitial lung disease RBILD is a syndrome of small airway inflammation and interstitial lung disease occurring in smokers.
The long-term outcome of interstitial lung disease with anti-aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase antibodies The long-term outcome of ARS-ILD was significantly better than that of IPF regardless of the presence or absence of myositis. Although the long-term survival of patients with ARS-ILD is better that of those with IPF ARS-ILD can be a progressive and fatal disease even with long-term IS therapies. It is a histological finding not a pathological description. A clinicopathologic study in current smokers ex-smokers and never-smokers. Symptoms include cough and breathlessness during exertion. And include in order of frequency central bronchial wall thickening 90 peripheral bronchial wall thickening 86 centrilobular. Respiratory bronchiolitis associated interstitial lung disease RB-ILD presenting with haemoptysis.



























Post a Comment for "Respiratory Bronchiolitis Interstitial Lung Disease Long Term Outcome"