Digeorge Syndrome Pharyngeal Pouch
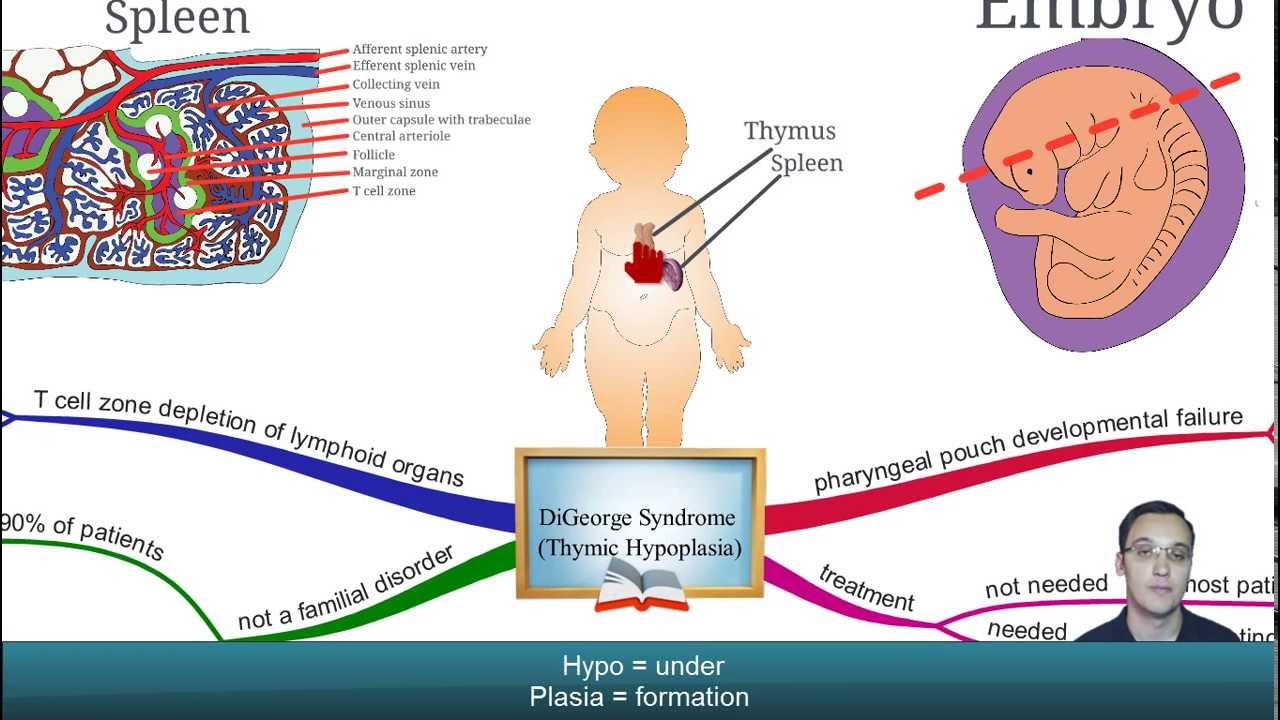
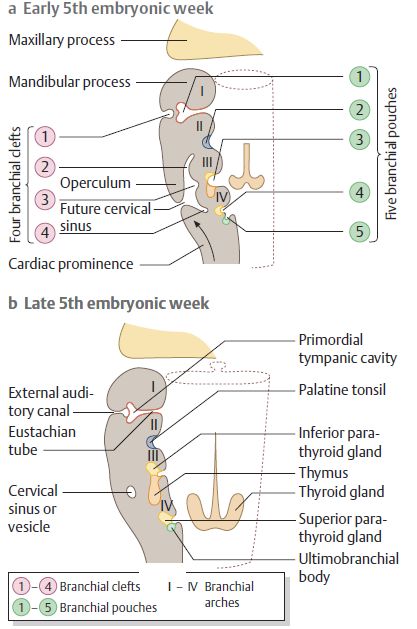
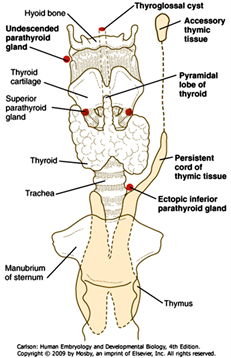
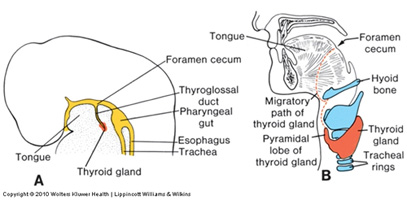
Digeorge syndrome pharyngeal pouch. DiGeorge syndrome DGS is a constellation of signs and symptoms associated with defective development of the pharyngeal pouch system. DiGeorge Syndrome Occurs because the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches fail to differentiate into the thymus and parathyroid glands Breakdown in signaling between pharyngeal endoderm and adjacent neural crest cells Clinically Congental Hypoparathyroidism Increased susceptibility to infection defective T-cells immune. Associated conditions include kidney problems hearing loss and autoimmune.
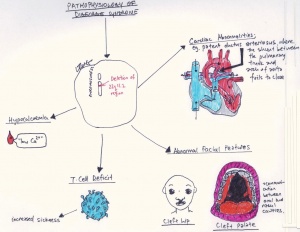
Partial or complete absence of the thymus DiGeorge syndrome III-IV pharyngeal pouch syndrome is often associated with agenesis or hypoplasia of the parathyroid glands and almost invariably with cardiovascular malformations. DiGeorge syndrome DGS is caused by developmental anomalies of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches and is characterized by thymic hypoplasia hypoparathyroidism conotruncal heart malformation especially interrupted aortic arch type B or truncus arteriosus and facial dysmorphisms micrognathia hypertelorism antimongoloid slant of the eyes cleft palate and ear. The anatomic characteristics of the heart defect suggest a possible mechanism for the pathogenesis of this developmental anomaly.
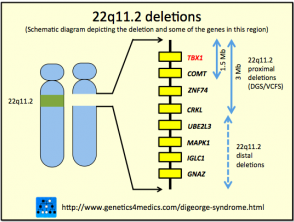
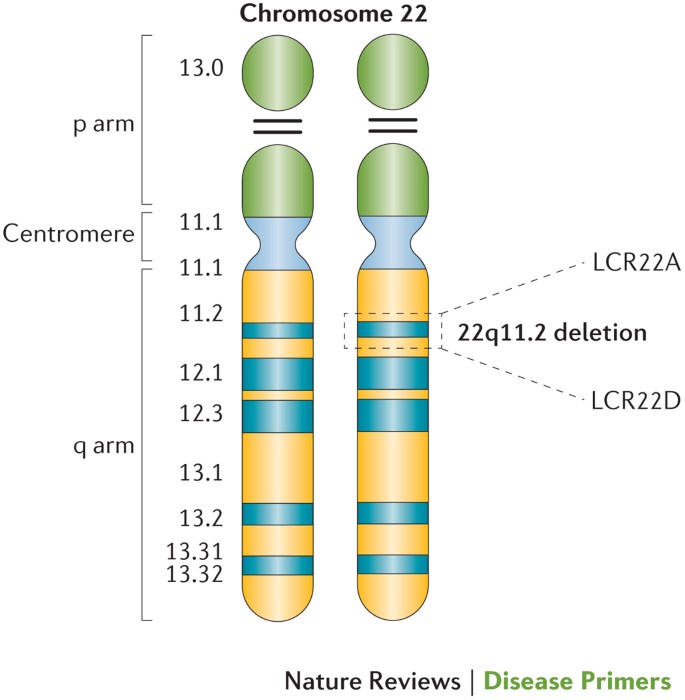
Chromosome 22q112 deletion syndrome. DiGeorge Syndrome Synonyms 22q11 deletion syndrome Velocardiofacial DiGeorge syndrome. Hypoplasia of thymus and parathyroid.
Most cases are caused by a heterozygous chromosomal deletion at 22q112. Tetralogy of Fallot and truncus arteriosus are associated with DiGeorge syndrome 22q11. Disturbance of cervical neural crest migration into the derivatives of the pharyngeal arches and pouches can account for the phenotype.
The classic triad of features of DGS on presentation is conotruncal cardiac anomalies hypoplastic thymus and hypocalcemia resulting from parathyroid hypoplasia. While the symptoms can vary they often include congenital heart problems specific facial features frequent infections developmental delay learning problems and cleft palate. DiGeorge syndrome also called 22q11 deletion syndrome congenital thymic hypoplasia or third and fourth pharyngeal pouch syndrome is a birth defect that is caused by an abnormality in chromosome 22 and affects the babys immune system.
Immunodeficiency Risks T-cell immunodeficiency is typical of the DiGeorge Syndrome and is the result of thymic hypoplasia. DiGeorge syndrome is a chromosomal disorder due to 22q112 deletion characterized by failure of development of the third to fourth pharyngeal pouches and fourth branchial arch which leads to a combination of congenital heart disease parathyroid abnormalities hypocalcemia and thymic abnormalities immunodeficiency. A developmental defect of derivatives of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches almost always associated with agenesis or hypoplasia of the thymus and parathyroid gland characteristic facies with downslanting palpebral fissures and ocular and nasal anomalies hypocalcemia cardiovascular anomalies immunodeficiency and other variable abnormalities.
It occurs due to 3 and 4th pharyngeal pouch affeced. DiGeorges on the IIblV pharyngeal pouch syndrome.
Transposition of the great arteries is associated with maternal diabetes.
All occurred in patients with conotruncal cardiac anomalies. DiGeorge syndrome DGS is a constellation of signs and symptoms associated with defective development of the pharyngeal pouch system. DiGeorge Syndrome Occurs because the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches fail to differentiate into the thymus and parathyroid glands Breakdown in signaling between pharyngeal endoderm and adjacent neural crest cells Clinically Congental Hypoparathyroidism Increased susceptibility to infection defective T-cells immune. DiGeorge syndrome also known as 22q112 deletion syndrome is a syndrome caused by the deletion of a small segment of chromosome 22. DiGeorge syndrome also called 22q11 deletion syndrome congenital thymic hypoplasia or third and fourth pharyngeal pouch syndrome is a birth defect that is caused by an abnormality in chromosome 22 and affects the babys immune system. DiGeorge syndrome is a chromosomal disorder due to 22q112 deletion characterized by failure of development of the third to fourth pharyngeal pouches and fourth branchial arch which leads to a combination of congenital heart disease parathyroid abnormalities hypocalcemia and thymic abnormalities immunodeficiency. DiGeorge syndrome is also called congenital thymic hypoplasia or third and fourth pharyngeal pouch syndrome because the congenital abnormalities occur in areas known as the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches which later develop into the thymus and parathyroid glands. It occurs due to 3 and 4th pharyngeal pouch affeced. A developmental defect of derivatives of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches almost always associated with agenesis or hypoplasia of the thymus and parathyroid gland characteristic facies with downslanting palpebral fissures and ocular and nasal anomalies hypocalcemia cardiovascular anomalies immunodeficiency and other variable abnormalities.
All occurred in patients with conotruncal cardiac anomalies. The clinical and pathologcial findings in 10 cases proven at necropsy. While the symptoms can vary they often include congenital heart problems specific facial features frequent infections developmental delay learning problems and cleft palate. Most cases are caused by a heterozygous chromosomal deletion at 22q112. Partial or complete absence of the thymus DiGeorge syndrome III-IV pharyngeal pouch syndrome is often associated with agenesis or hypoplasia of the parathyroid glands and almost invariably with cardiovascular malformations. DiGeorge syndrome presenting as severe congenital heart disease in the newborn Can Med Assoc J 116635 1977. GERD and pharyngeal and esophageal dysmotility can lead to an increased risk of aspiration which has been noted in a case report.





































Post a Comment for "Digeorge Syndrome Pharyngeal Pouch"